
Going green with your new home saves the planet and your wallet. As home shoppers explore potential builders, keeping energy efficient features in mind can help you build a home that stays comfortable, saves you money, and provides your family with a healthy environment for your new life.
The good news: it’s easy being green when you buy and build new. Major homebuilders understand that today’s shoppers are looking for energy-efficient features, and are consistently working to improve the quality of the home-building materials. Home shoppers can choose from a wide range of builders who deliver amazing homes that conform to national standards for energy efficiency, water conservation, and wellness features.
The bad news: it isn’t easy being green when you have to figure out what all the acronyms for all energy efficient programs mean. A wide range of green building programs means there are a number of acronyms and industry terms, and home shoppers must figure out what they each mean, what they measure or grade, and how it benefits homeowners and the planet.
NewHomeSource is here to help home shoppers understand all the different green home building programs and certifications, so you don’t get bowled over by all the acronyms.
ENERGY STAR

ENERGY STAR is a rating system run by the EPA (the U.S. environmental protection agency) and the Department of Energy. Most consumers think of an ENERGY STAR rating indicating that a home appliance has passed a stringent program testing its energy efficiency. While ENERGY STAR does rate home appliances for its ability to comply with energy saving principles, it also can rate the overall energy efficiency of a complete new home and commercial appliances and buildings.
DOE Zero Energy Ready Home

DOE Zero Energy Ready Home Program extends the benefits of the ENERGY STAR program to recognize homebuilders who go above and beyond in pursuing sustainability through their housing projects by improving energy efficiency and indoor air quality, while making homes zero energy ready.
HERS
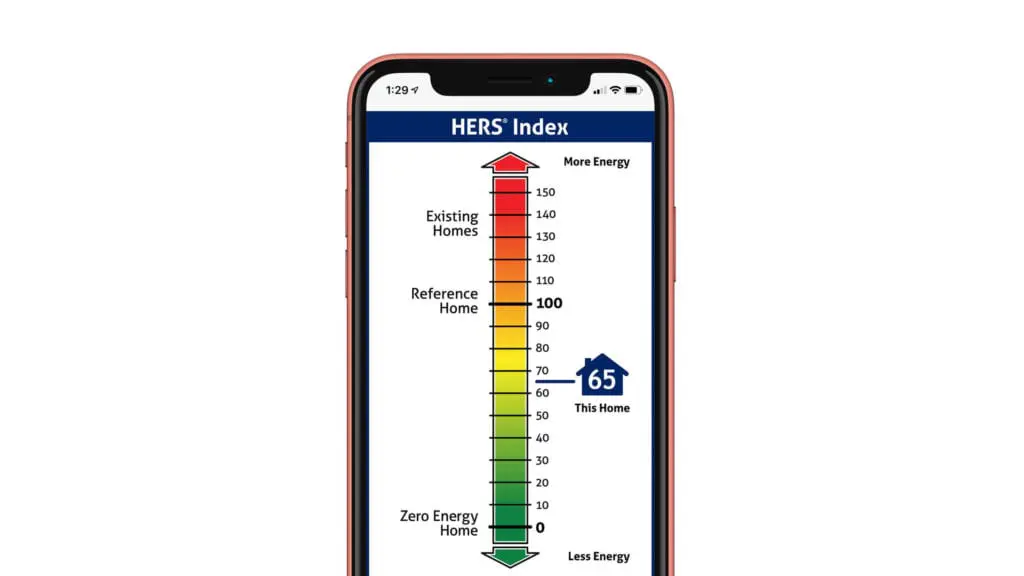
HERS (the Home Energy Rating System ) is an industry standard that measures how energy-efficient a home is. The score goes from 0 to 150, with a 0 rating indicating that the home is a Net Zero energy consumer. The average new construction home has a rating of 100, and the average used house has a score of 130.
Passive House

Passive House is a voluntary industry standard for green homebuilding that results in a home that uses a minimal amount of energy. The Passive House standard mostly focuses on energy savings in heating and cooling the home through features such as using a tight envelope around the home, well-sealed doors and windows, and high-quality insulation.
PHIUS+ Certification

The PHIUS+ Certification is the leading certification method for passive houses. For home shoppers interested in buying a passive house, the PHIUS+ Certification ensures that you invest in a home that actually meets the standards you care about.
Net-Zero
A Net-Zero house produces as much energy as it uses. You can build a Net-Zero house by using highly energy efficient materials and low water fixtures, and leveraging solar and wind power.

Indoor airPLUS

Indoor airPLUS is a voluntary labeling program sponsored by the EPA that helps builders improve the indoor air quality of a new construction home. A builder that meets the Indoor airPLUS building and material standards to create a healthy home. A home and builder that meets the Indoor airPLUS standard minimizes the mold, germs, allergens, and pollutants circulating in the house.
LEED

The LEED program (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) is the most widely used green building rating system in the entire world. LEED gives consumers and easy to understand tier program to determine the overall energy efficiency of a home. A home earns points for energy efficiency and green features, so the higher the LEED rating, the better the home is for your family and the planet.
National Green Building Standard™

The National Green Building Standard (NGBS) provides a thrid party conformation that a home conforms to a riggorus standard for green building. The NGBS focuses on six key aspects to building a green home:
- Site Design
- Resource Efficiency
- Water Efficiency
- Energy Efficiency
- Indoor Environmental Quality
- Operation & Maintenance
Living Building Challenge

The Living Building Challenge (LBC) flips the script on environmental standards for the construction industry. Instead of measuring harm mitigation and minimization, LBC measures how a dwelling improves the environment.
As you begin your journey to homeownership, green home features can really improve your quality of life. (We won’t judge you if you bring a green building BINGO card when you interview builders though!)

After graduating in 2016 from The University of Texas with a degree in English, Sanda Brown became a content writer for the BDX with a focus on website copy and content marketing.
At the BDX, Sanda helps write and edit articles on NewHomeSource.com, writes website copy for builders, and manages a team of freelancers that work on additional content needs.
 Everything You Need To Know About Energy-Efficient New Homes
Everything You Need To Know About Energy-Efficient New Homes